Describe the Structure of Red Blood Cells
This shape aids in a red blood cells ability to maneuver through tiny blood vessels to deliver oxygen to organs and tissues. Erythrocytes red blood cells or RBCs are anucleate biconcave cells filled with hemoglobin that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and tissues.
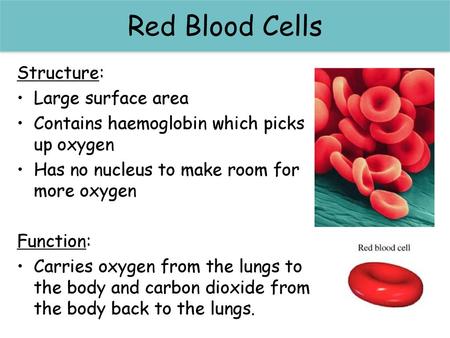
Red Blood Cells Red Blood Cells Structure Large Surface Area Ppt Video Online Download
Human red blood cells 68μm RBCs are disc-shaped with a flatter concave center.

. In humans the average red blood cell has a volume of only about 100 µm 3. Red blood cells are denser so they are span down to the bottom. List the two most important red blood cell RBC.
Red blood cells are round with a flattish indented center like doughnuts without a hole. Their relative amounts can be measured by the packed volume after the centrifugation. They have no nucleus so they can contain more haemoglobin.
Red blood cells dont have a nucleus like white blood cells allowing them to change shape and move throughout your body easier. However enzymes within the red blood cells allow it to produce small amounts of energy ATP from glucose. The mature human red blood cell is small round and biconcave.
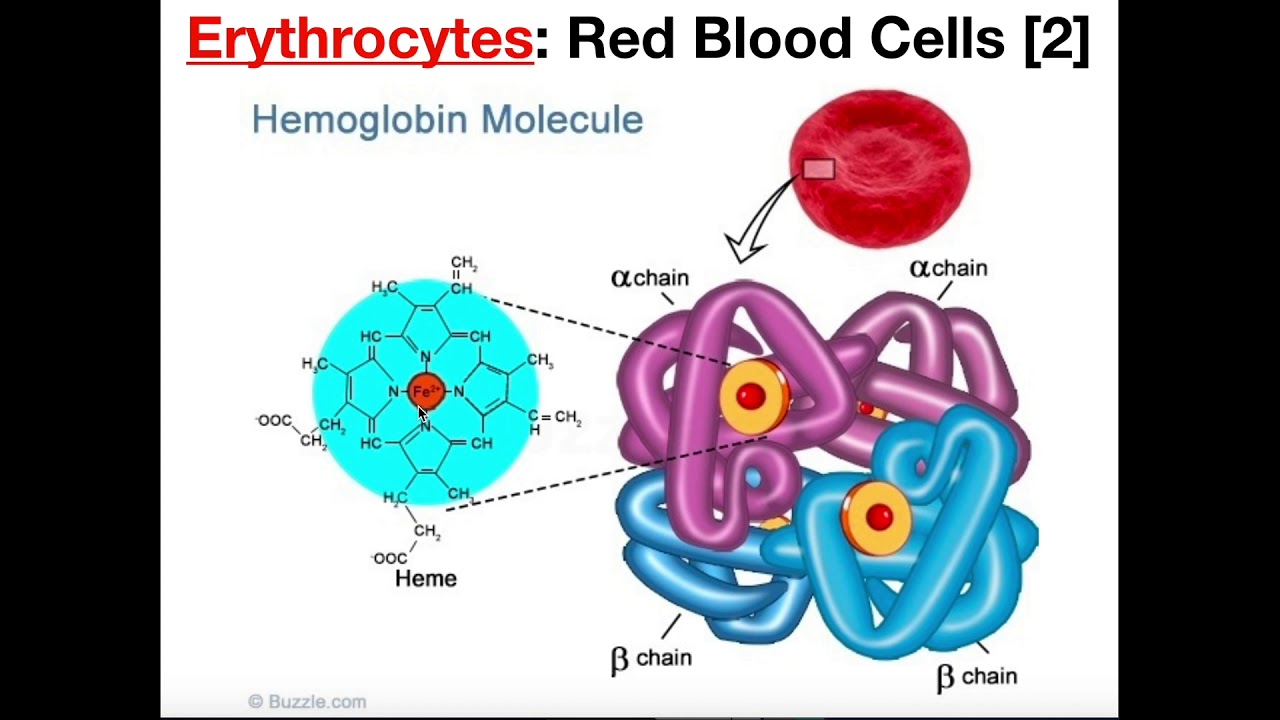
It lacks a nucleus mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum. Red blood cells RBCs carry oxygen bound reversibly to the ferrous Fe 2 atoms of the four haem groups of the haemoglobin Hb tetramer. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow.
The natural shape of the cell is that of a biconcave disk Fig. Red blood cells contain oxygen in their outer perimeter and none within the center resulting in their flattened disc-like shape. Plasma is lighter so it floats on the top.
Both sides of the cells surface curve inward like the interior of a sphere. The chemical composition of the membrane mass is approximately 40 lipids 52 proteins and 8 carbohydrates. Your healthcare provider can check on the size shape and health of your red blood cells using a blood test.
Its a big problem when red blood cells cant carry enough oxygen to meet the needs of body cells. Red blood cells are microscopic and have the shape of a flat disk or doughnut which is round with an indentation in the center but it isnt hollow. Unlike the other cells in the body red blood cells are made up of pigments known and hemoglobin composed of 4 hemes which gives erythrocytes the red color and a globin protein.
The shape can vary drastically with many different forms of red blood cells described in the literature. As a result the mature erythrocyte is among the smallest cells of the body. Describe the formation of the formed element components of blood provide the structure and function of red blood cells hemoglobin and classify and characterize whit blood cells.
Here the four hemes attach to a single protein to form a polypeptide chain. A red blood cell is sometimes simply referred to as a red cell. A genetic disease known as sickle cell anemia changes the hemoglobin transforming the red blood cells round biconcave shape into a longer thinner sickle like shape.
The diameter of a red blood cell. A red blood cell has what is known as a biconcave shape. As they mature RBCs extrude their nucleus and fill their cytoplasm with hemoglobin Hb molecules which bind and transport oxygen O2 and carbon dioxide CO2.
Red blood cell agglutination means that the cells are clumped together in a cluster and rouleaux refers to the erythrocytes arranged in a linear formation. In order to transport the Hb around the body in a functional state the RBC requires a flexible membrane and contents to pass passively through the capillary bed and a source of energy to maintain the internal milieu. Carbon dioxide nucleus Mature The shape of the cell allows oxygen exchange at a constant rate over the largest possible area low cellular hemoglobin convex The red blood cell is further adapted by lacking a Since possessing the following organelle requires large amounts of.
During this process stem cell derived erythroid precursors undergo a series of morphological changes to become. Between the plasma and RBCs is a thin layer of the white stuff called Buffy coat. Describe the chemical composition of the red cell membrane in terms of percentage of lipids proteins and carbohydrates.
Hemoglobin is the protein inside red blood cells. They are small and flexible so that they can fit through narrow blood vessels. Red blood cells contain numerous hemoglobin molecules resulting in their sickle-shaped appearance.
They have a biconcave shape flattened disc shape to. This biconcave shape allows the cells to flow smoothly through the narrowest blood vessels. Red blood cells have an unusual structure compared to other cells in the human body.
It appears dumbbell-shaped in profile. RBCs are small disc-shaped cells that measure 7 8 micrometers μm in diameter. Red blood cells at work.
It is also called an erythrocyte or rarely today a red blood corpuscle. Gas exchange with tissues occurs in capillaries tiny. Sickle Cell Anemia.
In mammals red blood cells are small biconcave cells that at maturity do not contain a nucleus or mitochondria and are only 78 µm in size. Erythrocytes also referred to as Red Blood Cells RBCs is a significant cellular component of blood. It is responsible for imparting blood with its characteristic colour.
Cyte cell are specialized cells that circulate through the body delivering oxygen to cells. Red blood cells contain numerous nuclei and are often filled with oxygen resulting in a round donut shape. These cells circulate in the blood carrying oxygen from the lungs to all the tissues of the body.
They are produced in the red bone marrow by a process called erythropoiesis. Describe the formation of the formed element components of blood provide the structure and function of red blood cells hemoglobin and classify and. 24-9 although the cell is flexible and its shape is easily distorted when the cell passes through narrow capillaries.
They are adapted to be round and flexible so it may pass through extremely small blood vessels. Red blood cells are also important in determining human blood type. Red blood cells or erythrocytes erythro red.
The most important part of a red blood cell is hemoglobin which is essentially the functional component of the cell. The RBC membrane hemoglobin structure and function metabolic pathways.
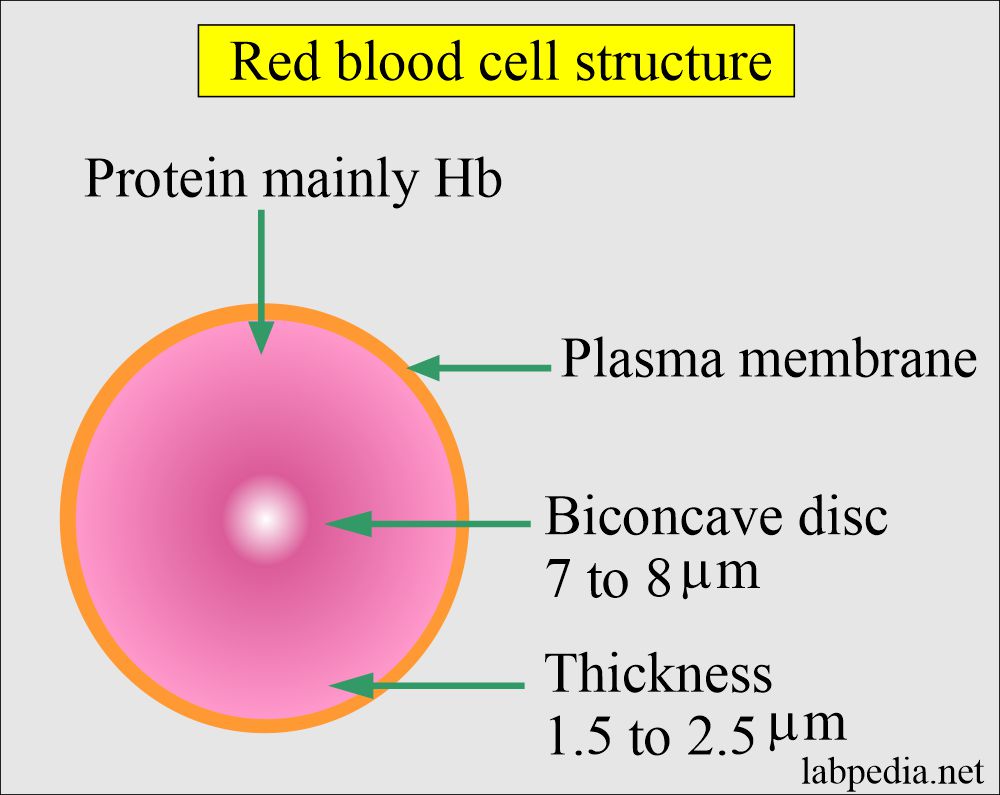
Complete Blood Count Red Blood Cell Morphology
No comments for "Describe the Structure of Red Blood Cells"
Post a Comment